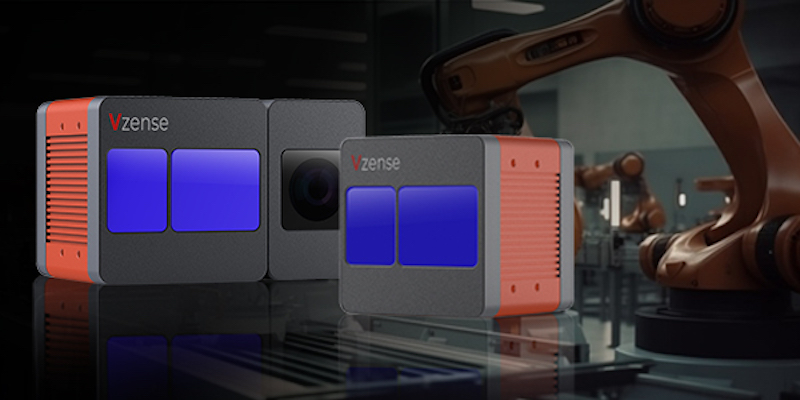
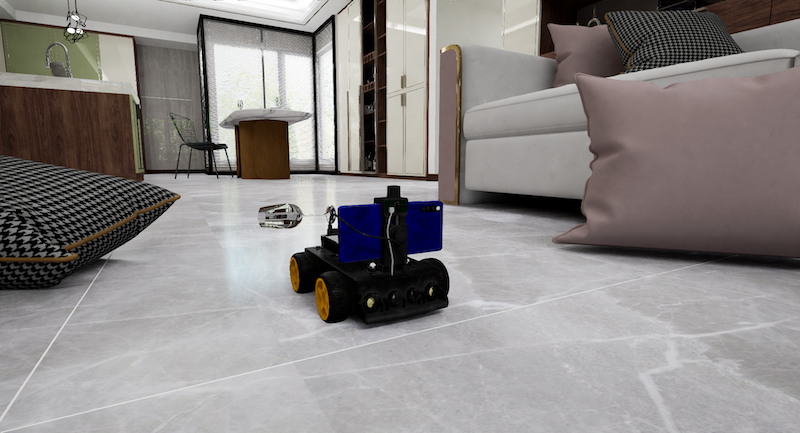
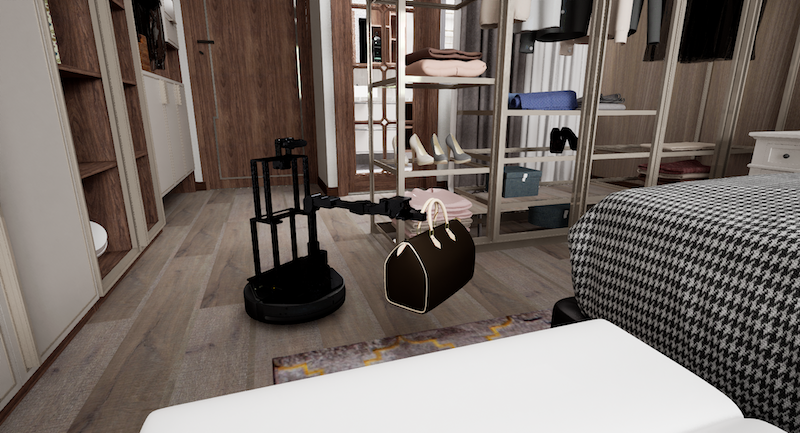
NEC – a large Japanese multinational information technology and electronics company – says it has developed AI technology for robotics that enables “precise handling operations on unorganized and disorderly placed items”.
By predicting both the areas hidden by obstacles and the results of a robot’s actions, this technology makes it possible for robots to perform tasks that were previously performed manually, thereby contributing to the improvement of productivity and work-styles.
In recent years, due to labor shortages and other factors, the need for automation through the introduction of robots and large-scale equipment has been increasing in logistics warehouses and factories. [Read more…] about NEC develops AI technology to enable robots to handle disorderly placed items