Automation is reshaping the landscape of electronics manufacturing. Today, nine out of ten manufacturers have already integrated some form of artificial intelligence into their operations, and the smart factory software market is projected to reach $97 billion by 2028.
This rapid technological shift has arrived at a critical time for the industry.
Manufacturers face a persistent labor shortage, with an estimated 500,000 to 600,000 open positions that remain difficult to fill. As a result, automation and intelligent systems have moved from being optional upgrades to essential tools for survival and growth.
Both local producers and global supply chains now experience measurable gains in precision, scalability, and operational efficiency, while human error and production delays continue to decline.
As the manufacturing world evolves, six transformative technologies stand at the forefront of progress. The following sections explore how these advancements are streamlining modern electronics production and defining the future of manufacturing.

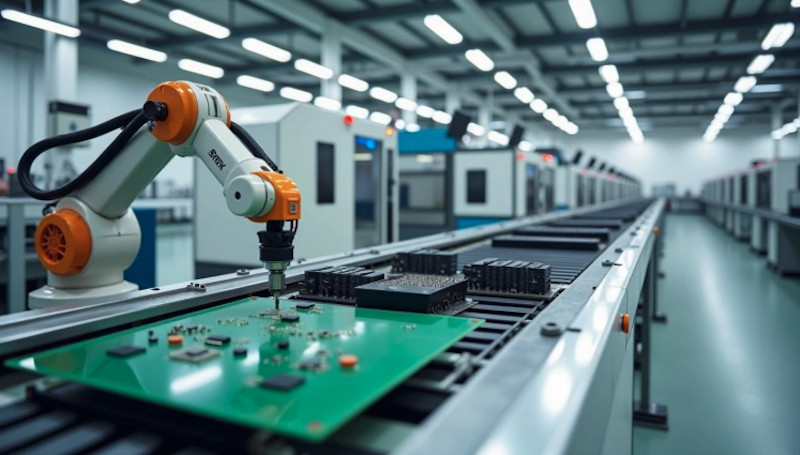
Automation and Robotics
Robotic systems are transforming electronics manufacturing worldwide. The industry now represents 28% of all new robot installations, with more than 103,000 units supplied for electronics applications in 2022.
Robots handle intricate, high-precision tasks once thought impossible to automate. Modern machines equipped with computer vision can place microscopic components with ±0.04 millimeter accuracy, reducing errors and improving quality.
Manufacturers increasingly rely on collaborative robots (cobots) to boost productivity. One factory saw a 25% increase in assembly line speed after introducing them. Automation delivers major advantages:
- Enhanced safety through reduced exposure to hazards
- Improved consistency across production
- Continuous operation for 24/7 productivity
- Live data analysis for process optimization
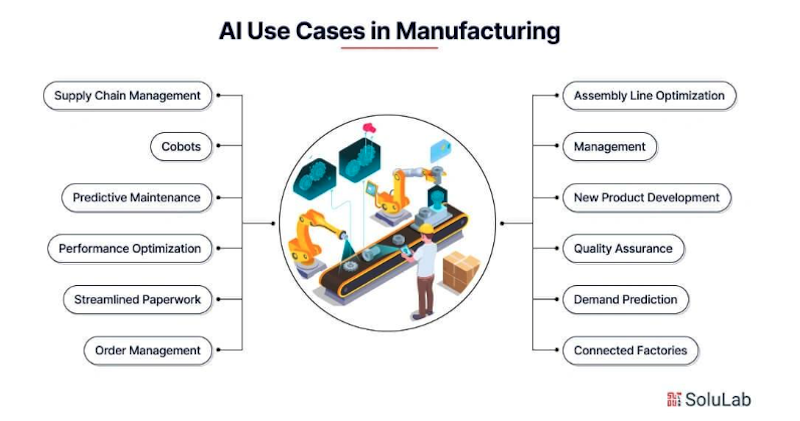
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are transforming electronics manufacturing beyond traditional automation. These technologies analyze massive data sets to detect patterns, predict outcomes, and improve production without manual programming.
AI-powered vision systems now identify surface flaws, cracks, and color variations invisible to the human eye, increasing product yield and cutting waste.
One manufacturer achieved a 30% boost in efficiency and a 97% yield using deep neural networks. The advantages of AI-driven quality control include:
- Enhanced accuracy that minimizes false detections
- Consistent results across inspections
- Live detection for immediate response
- Continuous learning that improves with new data
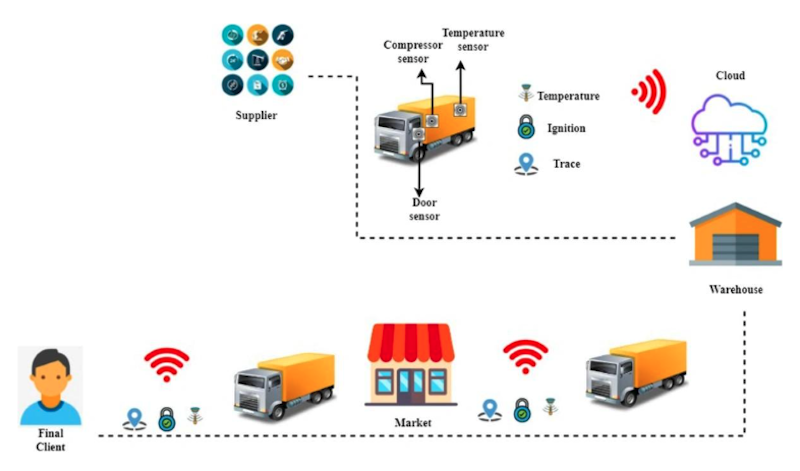
Smart Logistics and Electronics
Smart logistics plays a vital role in keeping modern electronics production efficient and reliable. Advanced tracking tools and automated warehouses now coordinate the flow of components between suppliers and assembly lines with remarkable precision.
Real-time monitoring allows manufacturers to track shipments continuously, ensuring sensitive materials remain protected during transit.
The advantages of intelligent logistics include:
- Prevention of costly damage through constant environmental monitoring
- Improved visibility across every shipment stage thanks to production management software
- Faster problem solving when disruptions occur
- Route optimization based on accurate tracking data
Companies like Greenwave Electronics provide specialized electronics 3PL solutions that make these systems even more effective.
Their expertise helps manufacturers lower costs, minimize waste, and build supply chains that keep up with the rapid pace of today’s electronics industry.
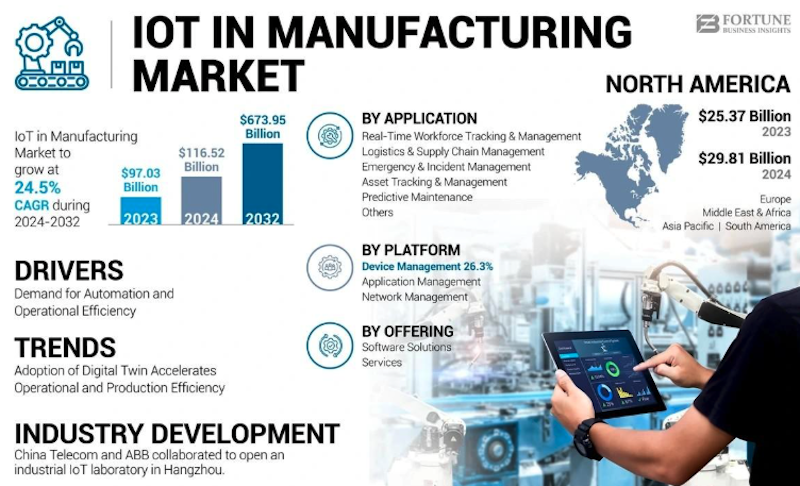
Internet of Things (IoT)
The Internet of Things (IoT) has become the central network connecting machines, people, and processes in modern electronics production. With sensors embedded across equipment, manufacturers gain access to real-time data on performance, energy use, and quality.
This constant stream of information helps managers make smarter, faster decisions that improve efficiency and reduce waste.
Among its many benefits, IoT enhances:
- Real-time monitoring to prevent equipment failures
- Quality control through continuous tracking
- Energy management that lowers operational costs
- Workplace safety using smart sensors and alerts
Advanced Printed Circuit Board Design
Advanced printed circuit board (PCB) design remains the core of every modern electronic device. New techniques have greatly improved manufacturing efficiency and product quality, allowing engineers to integrate design and production needs early in the process.
Design for Manufacturing (DFM) analysis now helps teams catch potential issues before production begins, saving time and reducing costly redesigns.
The key factors shaping advanced PCB design include:
- Board size and shape that define layout and component placement
- Material selection that affects performance and heat resistance
- Trace width and spacing that ensure signal integrity
Companies such as ACDI specialize in printed circuit board design services that combine precision, innovation, and manufacturability. Their expertise helps electronics manufacturers produce high-performance devices faster while maintaining reliability and cost efficiency.
Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)
Additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, is transforming electronics production by allowing the creation of complex, customized components that traditional methods cannot easily achieve.
This layer-by-layer process uses materials such as plastics, metals, and conductive inks to build detailed three-dimensional structures.
Key 3D printing methods include:
- Material extrusion for thermoplastic layering
- Material jetting for precise material placement
- Binder jetting for powder-based structures
- Powder bed fusion for strong, fused components
Conclusion
The evolution of modern electronics manufacturing reveals more than just technological progress – it reflects a complete transformation of how industries think, design, and deliver.
Each innovation, from robotics to additive manufacturing, creates ripple effects that push production closer to flawless precision and environmental responsibility.
The integration of intelligent systems allows manufacturers to make decisions rooted in real-time data, predict challenges before they escalate, and achieve greater consistency across global operations.
Factories are no longer just places of assembly; they are dynamic ecosystems where human expertise and machine intelligence work in sync.
As these six technologies continue to mature, their combined influence will redefine what efficiency means in electronics production.
The next chapter of this industry will be written not only through innovation but through the collaboration of technology, design, and smarter logistics working together toward a faster and cleaner future.

