Automating Patient Engagement: How Technology is Enhancing Healthcare Communication
Technology is changing how patients and doctors interact. New tools are making it easier for patients to take charge of their health and connect with providers.
This has the potential to improve care and outcomes. However, to realize the full benefits, we need to implement tech thoughtfully and focus on patients’ needs.
How Digital Solutions Empower Patients
Patient engagement means how involved someone is in managing their health. Research shows that engaged patients tend to have better results. So finding ways to get people more engaged should be a priority.
Technology can help with this. In 2020, about half of Americans used some form of health tech to communicate with their doctor. Patients are more likely to appreciate tech tools when they feel like their providers are partners in their care. As tech gives patients more ways to take part in their health, it makes sense that they’ll feel more invested.
Virtual visits are a big example. With virtual care, patients don’t have to take time off work or school and drive to the doctor’s office. This allows patients the ability to connect from anywhere.
This convenience makes people more comfortable interacting regularly. And that ongoing connection helps the doctor better understand the patient’s needs and guide their care.
How Healthcare Delivery is Modernizing
Healthcare has mainly centered on in-person hospital and clinic visits. When Covid-19 hit, most weren’t equipped to shift online. But out of necessity, telehealth use skyrocketed almost overnight in 2020. Providers realized that virtual care could work at scale.
Take Mercy Virtual Care Center. It gives patients 24/7 access to providers without having to go to a facility. This “care from anywhere” model brings healthcare into the modern digital age. It meets people’s expectations that services should revolve around their needs and lifestyles.
But telehealth is just one piece. To enable accessible, coordinated care, providers need tools to securely share medical information remotely. That’s where EHR software comes in.
This type of software creates a connected, shareable patient record across sites so doctors can collaborate. This integration is essential as care moves outside hospital walls.
Putting Patients at the Center of Care
In the past, healthcare was very provider-centric. Doctors made the decisions and patients did what they were told. But now patients are taking the lead in their care. This isn’t just a nice idea – it makes financial sense.
Studies show that giving patients the digital access they want could earn hospitals millions more a year. Tools that engage people in their health help providers meet consumer demands. That translates to a competitive advantage and a stronger bottom line.
Giving patients ownership of their care also improves health outcomes. Research shows that engaged individuals spend less on healthcare annually and have lower costs month-to-month. That’s because they’re more invested in taking preventive steps to avoid issues that require expensive care down the road.
Empowered patients want access to their full health records too. In 2008, only 10-15% of patients used online portals to view their charts. Today over 90% of Americans have registered for a patient portal. When people can easily access their test results and records, they can make more informed choices.
Using Tech to Predict Problems
Wearable devices and remote monitoring allow doctors to detect health changes early. If a patient’s heart monitor alerts their physician to an irregular heartbeat, they can intervene before it causes a stroke. By seeing issues brewing upstream, providers can be proactive.
Studies on patients taking inhaled medications found that those who got electronic reminders took over a third more doses than patients without reminders. Skipping doses leads to more emergency care. Simple reminders prevented many complications.
But remote monitoring tech isn’t accessible for all yet. One analysis showed that low-poverty areas had three times more telehealth visits compared to high-poverty regions. We need to close these care divides by creating low-cost options and training users in underserved communities.
AI and Big Data for Precision Medicine
Today advanced analytics tools can unlock insights from huge amounts of patient data. By using large datasets, algorithms can detect patterns that humans can’t. This allows earlier diagnosis, personalized treatment plans, and better-coordinated care.
For instance, AI now helps doctors search medical records in seconds to find candidates for clinical trials. This process used to take months. Applied Materials developed an AI-based tool that slashes the time needed to analyze prostate cancer images from 30 minutes to 30 seconds. That allows doctors to make faster diagnoses.
At CHI Franciscan, AI has cut hospital bed request response times by 80% and average stay by 11%. It reduces delays and waste. And these are just a handful of examples. AI will become integral to preventive, personalized medicine.
However, there are valid concerns about AI. Studies have found some AI missed cancers at much higher rates than human specialists. We have to be careful that tech augments human expertise rather than fully replacing it. Ongoing oversight will be key.
How Extended Reality Will Transform Medicine
Extended reality or XR includes virtual reality, augmented reality, and mixed reality tools that meld digital and physical environments. These technologies create new ways to deliver care and train providers.
XR surgical simulations allow doctors to do “test runs” of procedures before operating. Surgeons can visualize individual patient anatomy in vivid 3D. Studies show these realistic models boost surgical skills.
Augmented reality overlays digital data onto patients during procedures so doctors can operate without looking away. This eye contact puts patients at ease.
For patients, VR therapy lets people virtually confront fears and traumas in a safe setting. VR also reduces pain by immersing patients in engaging worlds.
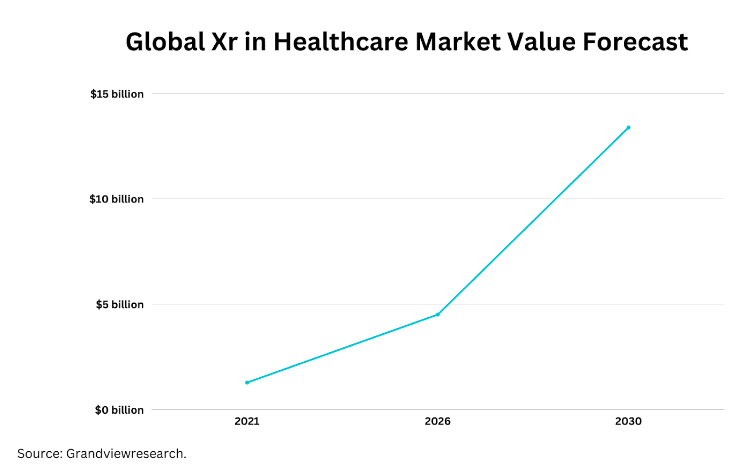
One researcher who suffered burns treated his pain with a VR snowball fight! As VR and AR mature, more therapeutic applications will emerge. The global XR healthcare market is projected to grow over 20% annually through 2030.
Connecting Systems to Connect Providers and Patients
Tools like Wellbe integrate data from apps, wearables, monitors, and EHRs onto a single platform. This gives doctors an accurate, real-time view of each patient for proactive care. Seamless data sharing also saves providers time spent manually gathering records and updating multiple systems.
But these technologies are only as good as the user experience. If systems are confusing or disconnected, doctors won’t use them. Intuitive design is crucial. Cybersecurity is also a concern. Over 80% of healthcare IT leaders reported a cyberattack last year. Maintaining bulletproof data protection and privacy will build patient trust.
This new era of care will require a culture shift. Providers, staff, and patients need education on how to navigate new tech-enabled workflows. However, when used thoughtfully, health tech will open new doors to convenient, collaborative, patient-driven care.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can virtual hospitals expand access to care?
Virtual hospitals use digital platforms to offer medical services remotely. This provides patients more flexibility in accessing care without physically traveling to a hospital.
What are the potential risks of artificial intelligence in healthcare?
Risks include perpetuating biases, privacy concerns over data sharing, lack of transparency, and potential errors. Careful testing and oversight are required to ensure AI safely enhances healthcare.
How can healthcare providers implement technologies equitably?
Providers must consider community needs, offer resources/training in technology use, provide both high-tech and low-tech options, and routinely assess for disparities in access and outcomes.
Technology is undoubtedly enhancing healthcare communication and patient engagement. But thoughtful implementation focused on consumer needs and equitable access is key to realizing its full transformative potential.
As patients become partners in their care, the future of healthcare will be defined by connectivity, intelligence, and patient empowerment.

