The Impact of Laser Cleaning Machines in the Aerospace Industry
Shining a light on the future, laser cleaning machines are revolutionizing the aerospace industry. Their ability to cleanly and efficiently remove contaminants has made these machines an essential tool in maintaining aircraft.
This article dives deep into the fascinating world of laser cleaning technology, revealing its multifaceted applications in aerospace.
Understanding Laser Cleaning Machines
Laser cleaning machines, also known as laser ablation systems, are a contemporary marvel of technology, utilizing light energy for precision cleaning. They work by directing a high-intensity laser beam at a surface, vaporizing the contaminant layer without damaging the underlying material.
These machines have gained prominence for their eco-friendly, non-contact cleaning approach, making them an ideal solution for the sensitive procedures required in the aerospace industry.
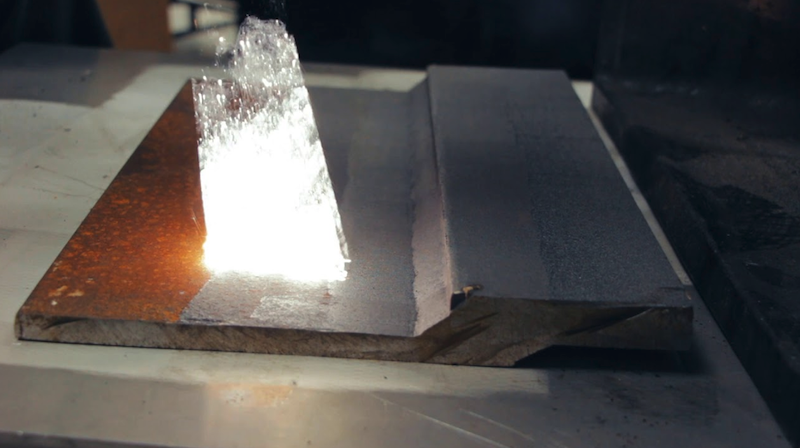
Surface Preparation and Maintenance
Surface preparation and maintenance is a crucial aspect of aerospace operations. Laser cleaning machines have proven to be remarkably effective in these procedures.
Removing Paint and Oxide Layers
Aerospace components often require paint or oxide layers to be removed for maintenance or repainting. Traditional methods can be slow, damaging, and environmentally unfriendly.
Laser cleaning machines, however, can efficiently remove these layers without the use of harsh chemicals or manual labor. They offer a cleaner, faster, and more controlled process, ensuring the integrity of the underlying surface.
Rust and Corrosion Removal
Aircraft are highly susceptible to rust and corrosion due to environmental exposure. Laser cleaning machines can target these corrosive elements without damaging the aircraft’s structure. This not only helps extend the lifespan of the aircraft but also prevents potential safety issues.
Inspection and Non-Destructive Testing
One of the significant applications of laser cleaning machines in aerospace is in the field of inspection and non-destructive testing (NDT).
Preparing Surfaces for Inspection
Before any inspection or NDT procedure, the surface under consideration needs to be impeccably clean. Laser cleaning machines can provide this level of cleanliness, facilitating a more accurate inspection.
Facilitating Non-Destructive Testing
In the realm of non-destructive testing, laser cleaning helps reveal flaws or defects in aircraft components. It can also be used in processes like ultrasonic testing and penetrant testing, where a clean surface is critical for accurate results.

Enhancing Safety and Efficiency
Safety and efficiency are paramount in the aerospace industry. Laser cleaning machines contribute significantly to these aspects.
Reducing Hazardous Waste
Traditional cleaning methods often produce hazardous waste. Laser cleaning, on the other hand, significantly reduces this problem. The process generates minimal waste, making it a greener alternative that aligns with sustainability goals.
Increasing Operational Efficiency
Laser cleaning machines are highly efficient, reducing the time required for cleaning processes. This increased efficiency can lead to reduced aircraft downtime and higher operational readiness, directly impacting the bottom line.
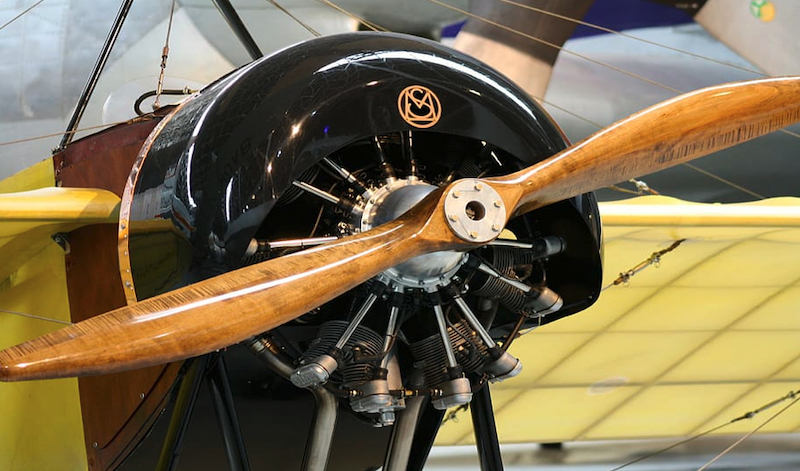

Restoring Historic Aircraft
Another intriguing application of laser cleaning machines in the aerospace industry lies in the restoration of historic aircraft.
Preserving Authenticity
Historic aircraft are not just machines; they are time capsules, echoing stories of past triumphs and challenges. Preservation of their authenticity is paramount during restoration. Laser cleaning machines allow for gentle cleaning of these precious artifacts, removing decades of accumulated grime without damaging the original material.
Revealing Hidden Details
Hidden details, obscured by layers of paint and corrosion, can be revealed using laser cleaning. This non-abrasive technique helps in unveiling original markings or construction details, providing valuable insights into the aircraft’s history.
Preparing for Coating Applications
In the aerospace industry, various components require protective coatings for longevity and performance. Laser cleaning machines play a vital role in preparing these surfaces.
Achieving Uniform Surface Profile
For a coating to adhere properly, the surface profile must be uniform and free of contaminants. Laser cleaning machines provide a precise and controlled cleaning process, achieving the desired surface profile without the risk of over-processing.
Enhancing Adhesion of Coatings
By effectively removing surface contaminants, laser cleaning promotes better adhesion of coatings. This results in a more durable and long-lasting protective layer, crucial for aerospace components exposed to extreme conditions.
Mold and Fungi Removal
Aircraft, particularly those in long-term storage or humid environments, can become breeding grounds for mold and fungi. Laser cleaning machines can effectively address this issue.
Non-Damaging Mold Removal
Laser cleaning provides a non-damaging solution for mold removal. It can eliminate mold and fungi without the need for harsh chemicals or abrasive techniques that could harm the aircraft’s material.
Preventing Mold Recurrence
By thoroughly removing mold and its spores, laser cleaning can help prevent recurrence, ensuring the aircraft remains safe and clean for longer periods.
Ever More Pivotal
In conclusion, the laser cleaning machines are not just a technological marvel; they are a transformative tool for the aerospace industry. Their diverse applications, from the restoration of historic aircraft to mold and fungi removal, showcase their versatility and effectiveness.
As we continue to push the boundaries of what’s possible in aerospace, the role of laser cleaning machines is set to become ever more pivotal, driving safety, efficiency, and preservation in this sky-reaching sector.

