Robotic pollinator: A fairy-like robot flies by the power of wind and light
The loss of pollinators, such as bees, is a huge challenge for global biodiversity and affects humanity by causing problems in food production. At Tampere University, researchers have now developed the first passively flying robot equipped with artificial muscle. Could this artificial fairy be utilised in pollination?
The development of stimuli-responsive polymers has brought about a wealth of material-related opportunities for next-generation small-scale, wirelessly controlled soft-bodied robots.
For some time now, engineers have known how to use these materials to make small robots that can walk, swim and jump. So far, no one has been able to make them fly.
Researchers of the Light Robots group at Tampere University are now researching how to make smart material fly. Hao Zeng, Academy Research Fellow and the group leader, and Jianfeng Yang, a doctoral researcher, have come up with a new design for their project called FAIRY – Flying Aero-robots based on Light Responsive Materials Assembly. They have developed a polymer-assembly robot that flies by wind and is controlled by light.
“Superior to its natural counterparts, this artificial seed is equipped with a soft actuator. The actuator is made of light-responsive liquid crystalline elastomer, which induces opening or closing actions of the bristles upon visible light excitation,” explains Hao Zeng.
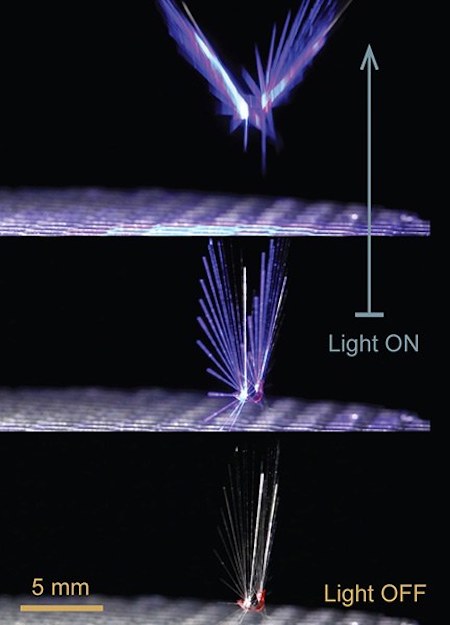
The artificial fairy is controlled by light
The artificial fairy developed by Zeng and Yang has several biomimetic features. Because of its high porosity (0.95) and lightweight (1.2 mg) structure, it can easily float in the air directed by the wind. What is more, a stable separated vortex ring generation enables long-distance wind-assisted travelling.
“The fairy can be powered and controlled by a light source, such as a laser beam or LED,” Zeng says.
This means that light can be used to change the shape of the tiny dandelion seed-like structure. The fairy can adapt manually to wind direction and force by changing its shape. A light beam can also be used to control the take-off and landing actions of this polymer assembly.
Responsive polymer allows the creation of artificial, autonomously operating structures. In dark and calm weather, the fairy stays still. When there is enough light, the structure opens automatically allowing flying in the wind flow.
Potential application opportunities in agriculture
Next, the researchers will focus on improving the material sensitivity to enable the operation of the device in sunlight. In addition, they will up-scale the structure so that it can carry micro-electronic devices such as GPS and sensors as well as biochemical compounds.
According to Zeng, there is potential for even more significant applications.
“It sounds like science fiction, but the proof-of-concept experiments included in our research show that the robot we have developed provides an important step towards realistic applications suitable for artificial pollination,” he reveals.
In the future, millions of artificial dandelion seeds carrying pollen could be dispersed freely by natural winds and then steered by light toward specific areas with trees awaiting pollination.
“This would have a huge impact on agriculture globally since the loss of pollinators due to global warming has become a serious threat to biodiversity and food production,” Zeng says.
Many questions remain to be answered
However, many problems need to be solved first. For example, how to control the landing spot in a precise way? How to reuse the devices and make them biodegradable? These issues require close collaboration with materials scientists and people working on microrobotics.
The FAIRY project started in September 2021 and will last until August 2026. It is funded by the Academy of Finland. The flying robot is researched in cooperation with Dr. Wenqi Hu from Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems (Germany) and Dr. Hang Zhang from Aalto University.
The article Dandelion-Inspired, Wind-Dispersed Polymer-Assembly Controlled by Light by Jianfeng Yang, Hang Zhang, Alex Berdin, Wenqi Hu, and Hao Zeng was published in Advanced Science on Dec 27 in 2022.

