Telerobotics: A ’smart’ remedy for productivity during Covid-19
By Neil Tardella, CEO, Energid
A surgeon in New York performs a robot-assisted surgery on a patient in India. An engineer in London programs and monitors a robotic work cell in Shenzhen, China.
An assembly line worker or welder unable to enter their auto manufacturing factories in Michigan performs their job remotely, with robots aiding in the process.
It’s called telerobotics – the area of robotics focused on controlling robots from a distance – and it’s bound to play an increasingly important role in society in the wake of the Covid pandemic.
The ability to decouple a human brain from a robot that can physically interact with its environment can be transformative, especially as we look to maintain productivity while keeping a distance from others.
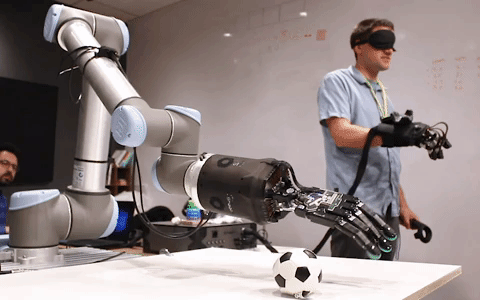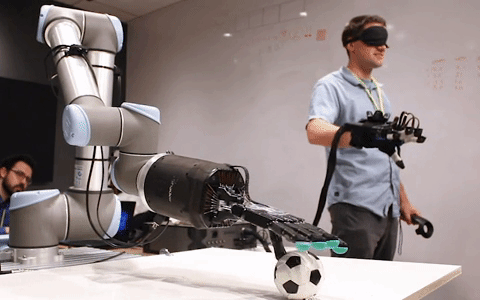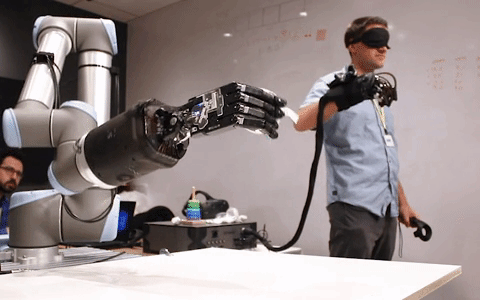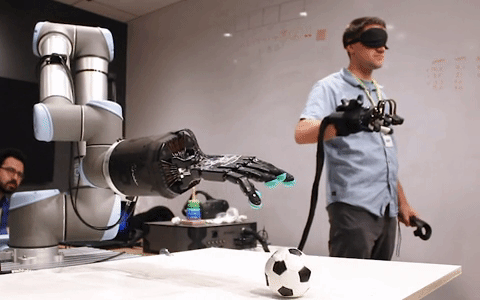
Telerobotics solutions from healthcare to manufacturing
Many countries were caught unprepared at the peak of the Covid-19 outbreak, resulting in overrun hospitals struggling with shortages of qualified healthcare providers and personal protective equipment (PPE).
Had hospital-based telerobotic solutions with remote controls been available, healthcare workers could have stepped off the frontlines and out of reach of the virus.
The systems could be used for medical material handling and diagnostics, such as taking a patient’s vital signs or administering vitally needed Covid-19 tests. Being able to deploy this type of technology now will prepare us for the next crisis.
Robotic telehealth solutions are valuable for many medical applications off the frontline as well, including diagnostic ultrasounds remotely controlled by an ultrasound technician or radiologist.
Not long ago, Energid worked with a startup developing such a system for medical kiosks, where patients could go to a local kiosk to get a carotid ultrasound performed by a remote technician.
Manufacturers benefit from telerobotics as well, especially in today’s environment, where factories can no longer be tightly packed with workers.
Industrial robots that can be remotely controlled, programmed and monitored can help reduce human density – still keeping a significant percentage of the workforce – without the commensurate reduction in productivity.
Do we have what it takes now for widespread use?
Developing a telerobotic solution that injects human intelligence, environmental awareness and real-time response into automation systems requires careful planning and some key technology enablers. These include the ones listed below.
Safe robots: Robots designed for remote operation have less onsite support to fix problems, apply preventive maintenance, and reset controllers. The robots may also have contact with humans who are not familiar with them, such as with patients and technicians in telehealth situations, or workers in a manufacturing facility.
Robots with built-in safety mechanisms protect nearby humans as well as the robot and equipment around it. Starting with a robot that is fundamentally safe – such a collaborative robot (‘cobot’) that already has extensive safety features built in – reduces the chance of a catastrophic system failure and makes building the system less complex.
Software can add another layer of safety for remotely operated robots by allowing the remote operator to create virtual ‘keep-out’ zones. The keep-out zones prevent the operator from unintentionally moving the robot into an area containing fragile equipment, for instance. Advanced real-time adaptive software can also be used to make sure the robot can’t collide with itself – something that often happens during remote programming and less-structured applications.
Remote-control infrastructure: Controlling a robot remotely requires an infrastructure that supports two-way communication between the remote operator, the robot and any tools required for the procedure. This is more than a connectivity or bandwidth issue. In fact, high-speed internet and today’s 4G and 5G technologies are highly capable for telerobotics.
What’s harder to come by is software that translates high-level operator commands to low-level robot and tool commands. The infrastructure must be flexible enough to support all the modes of operation for a telerobot, and it should be capable of communicating enough data to the remote operator to give sufficient situational awareness of the environment.
This typically means streamed high-resolution video, at a minimum. Often multiple cameras from multiple vantage points are used so the operator can see the work cell from multiple vantage points. In some situations, tactile (or force) feedback can be conveyed back to the remote operator.
The fidelity of the data, latency and modalities required are highly application-dependent. A remote surgical robot, for instance, will require more data and lower latency than a fully autonomous work cell that requires only intermittent monitoring.
Intuitive operator interface: Early telerobot systems required operators to turn a series of knobs on the input device to move each joint in the remote robot. Such systems were difficult to use and didn’t scale well, especially when the robot had more than a few joints.
Today, software can translate simple, intuitive human gestures into meaningful robot motions that feel natural. This is critical in situations such as surgical robots, which need the remote operator interface to feel as natural and intuitive as performing the surgery without a robot, with software that can iterate many times on the control strategies to ensure the operator has immediate, intuitive control and feedback.
To get these natural, human-life movements, the operator interface can only be as good as the robot control strategies allow it to be. A robot may have many joints or just a few, but in almost every case the kinematics (that is, the articulated structure) of a robot differs materially from that of a person. This makes mapping a person’s control intentions to the motion of a robot no easy task.
Robotic developers who have an enabling robot control system need to pay special attention to developing the actual operator interface, which is what the remote operator will interact with.
Because the operator knows how to perform the task being teleroboticized but not much about robotics, telerobotic interfaces are almost always designed specifically for each unique application. Successful operator interfaces require significant testing and iteration.
A comprehensive simulation environment can reproduce what the remote operator will see, how the robot will move, and even the latency inherent in the remote connection. This significantly reduces development time as well as risk in complex telerobotic applications.
Adaptive real-time software enables the enablers
Software can play a critical role in supporting all three telerobotic “enablers.” Advanced real-time adaptive software, in particular, can simulate many telerobotic systems, including space-based and undersea applications, where latency and automatic collision detection play a critical role.
It can also allow a physical remote robotic work cell to be replaced by an interactive graphical simulation, allowing developers to test the operation of their telerobotic application without the need to procure or fabricate hardware.
Advancements with this enabling technology, and an increased knowledge of the capabilities offered, should encourage the implementation of telerobotics across myriad industries as the pandemic continues – and long into the future.
Technologies worked with co-founders Dr Jeff Soble and Sarah Doherty of startup TeleHealthRobotics to develop a system for medical kiosks, where patients could go to a local kiosk to have a carotid ultrasound performed by a remote technician. In the video above, the subject was in Chicago and the operator was in Boston.
About the author: Neil Tardella is the CEO at Energid. He has spearheaded commercial initiatives in the energy, medical, and collaborative robotics sectors. Prior to joining Energid, Neil held key research and development and management roles at Northrop Grumman Norden Systems, Sikorsky, and Technology Service Corporation.

