The University of Portsmouth scientists who re-engineered the plastic-eating enzyme PETase have now created an enzyme “cocktail” which can digest plastic up to six times faster.
A second enzyme, found in the same rubbish dwelling bacterium that lives on a diet of plastic bottles, has been combined with PETase to speed up the breakdown of plastic.
PETase breaks down polyethylene terephthalate (PET) back into its building blocks, creating an opportunity to recycle plastic infinitely and reduce plastic pollution and the greenhouse gases driving climate change.
PET is the most common thermoplastic, used to make single-use drinks bottles, clothing and carpets and it takes hundreds of years to break down in the environment, but PETase can shorten this time to days.
The initial discovery set up the prospect of a revolution in plastic recycling, creating a potential low-energy solution to tackle plastic waste. The team engineered the natural PETase enzyme in the laboratory to be around 20 percent faster at breaking down PET.
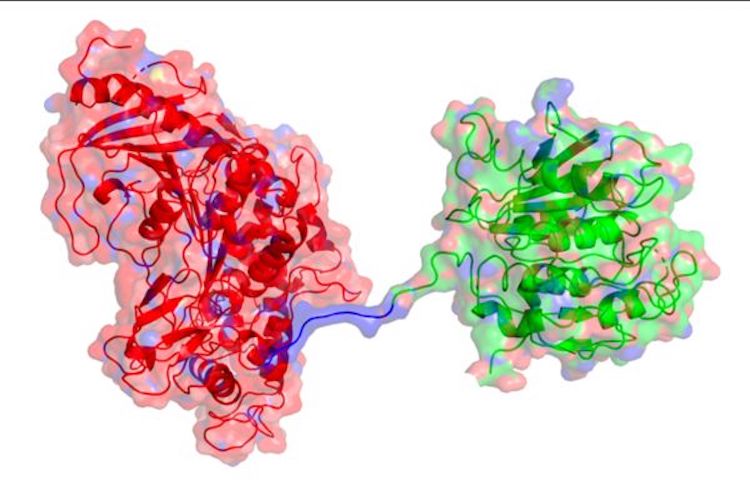
Now, the same trans-Atlantic team have combined PETase and its “partner”, a second enzyme called MHETase, to generate much bigger improvements: simply mixing PETase with MHETase doubled the speed of PET breakdown, and engineering a connection between the two enzymes to create a “super-enzyme”, increased this activity by a further three times.
The study is published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
The team was co-led by the scientists who engineered PETase, Professor John McGeehan, Director of the Centre for Enzyme Innovation (CEI) at the University of Portsmouth, and Dr Gregg Beckham, Senior Research Fellow at the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) in the US.
Professor McGeehan said: “Gregg and I were chatting about how PETase attacks the surface of the plastics and MHETase chops things up further, so it seemed natural to see if we could use them together, mimicking what happens in nature.
“Our first experiments showed that they did indeed work better together, so we decided to try to physically link them, like two Pac-men joined by a piece of string.
“It took a great deal of work on both sides of the Atlantic, but it was worth the effort – we were delighted to see that our new chimeric enzyme is up to three times faster than the naturally evolved separate enzymes, opening new avenues for further improvements.”
The original PETase enzyme discovery heralded the first hope that a solution to the global plastic pollution problem might be within grasp, though PETase alone is not yet fast enough to make the process commercially viable to handle the tons of discarded PET bottles littering the planet.
Combining it with a second enzyme, and finding together they work even faster, means another leap forward has been taken towards finding a solution to plastic waste.
PETase and the new combined MHETase-PETase both work by digesting PET plastic, returning it to its original building blocks. This allows for plastics to be made and reused endlessly, reducing our reliance on fossil resources such as oil and gas.
Professor McGeehan used the Diamond Light Source, in Oxfordshire, a synchrotron that uses intense beams of X-rays 10 billion times brighter than the Sun to act as a microscope powerful enough to see individual atoms. This allowed the team to solve the 3D structure of the MHETase enzyme, giving them the molecular blueprints to begin engineering a faster enzyme system.
The new research combined structural, computational, biochemical and bioinformatics approaches to reveal molecular insights into its structure and how it functions. The study was a huge team effort involving scientists at all levels of their careers.
One of the most junior authors, Rosie Graham, a joint Portsmouth CEI-NREL PhD student said: “My favourite part of research is how the ideas start, whether it’s over coffee, on a train commute or when passing in the university corridors it can really be at any moment.
“It’s a really great opportunity to learn and grow as part of this UK-USA collaboration and even more so to contribute another piece of the story on using enzymes to tackle some of our most polluting plastics.”
The Centre for Enzyme Innovation takes enzymes from the natural environment and, using synthetic biology, adapts them to create new enzymes for industry.