Autonomous shuttles: Large, diesel buses being replaced with electric, self-driving shuttles
The autonomous mobility industry is tackling part of the last-mile problem that many commuters encounter when using public transportation by replacing large, diesel buses with a fleet of electric, self-driving shuttle buses that transport small groups of people along defined and planned routes.
Autonomous shuttles could be a key element that connects the public transportation systems to reduce private car ownership in the future.
The autonomous shuttle total market size will be over $18 million by 2040, according to IDTechEx’s report, Robot Shuttles and Autonomous Buses 2020-2040.
Autonomous shuttles are upright, boxy, 8-20 person vehicles that are symmetrical so they never do a U-turn. Small footprint, all-round vision, large doors, quiet, zero-emission, they can go indoors and over piazzas and roads and are able to perform many different tasks even in one day.
Primarily intended for intensive urban use, they are gated to never exceed a determined speed, typically in the range 50-60 kmph.
It all adds up to a new form of transport backed by both huge companies like Toyota and Baidu and start-ups alike. Their trials explore many possible applications, from empowering the poor and disabled, to viably filling in gaps in the transportation network and replacing very underutilized vehicles such as school buses and private cars, reducing congestion and cost.
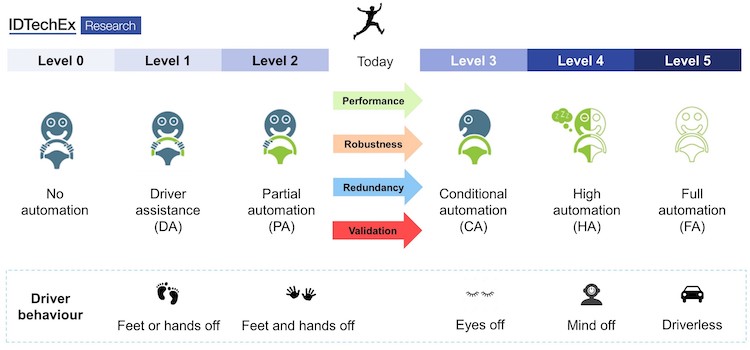
In IDTechEx’s new report Electric, Hybrid and Fuel Cell Buses 2021-2040, the major players developing autonomous shuttles are profiled. We summarise a selection of these companies below. While true level 4 autonomy does not currently exist, most companies discussed are at ‘level 4’ in geofenced or controlled areas.
Navya is a French company founded in 2014 with over 270 employees in France and the US. The company filed for IPO in Euronext Paris in July 2018 with 80 million euro ($94 million) financing and the company achieved 19 million euro ($22 million) revenues in 2018.
The Autonom Shuttle (main picture), launched in 2015, is designed for a low-speed environment where there is a high frequency of travel. Currently, it is still operated at Level 3 autonomy where on-board safety operators are required.
The shuttle is dedicated to the first and last-mile transportation and can carry up to 15 people. The shuttle is suitable for underserved areas where full-sized buses might not be justified from a ridership standpoint, or areas that are too tight to get around.
The shuttles can operate on open roads in cities or private sites such as campuses, business parks, airports, industrial parks and hospitals – anywhere where people are taking lots of trips from half a mile up to two miles.
Navya’s strategy is to build small autonomous shuttles with a $300,000+ price that can be amortized over time by municipalities, campuses and large corporate parks working on smart city projects.

EasyMile is a French high-tech start-up founded in 2014 with over 180 employees. The main product, EZ10, was designed from the ground for autonomous driving (no steering wheel).
The EZ10 was launched in 2015 and 110 units have been sold to date. The company is generating some revenues (relatively small) from selling the shuttles. Apart from selling the EZ10 shuttles, the company also licenses its in-house autonomous driving software to other companies.
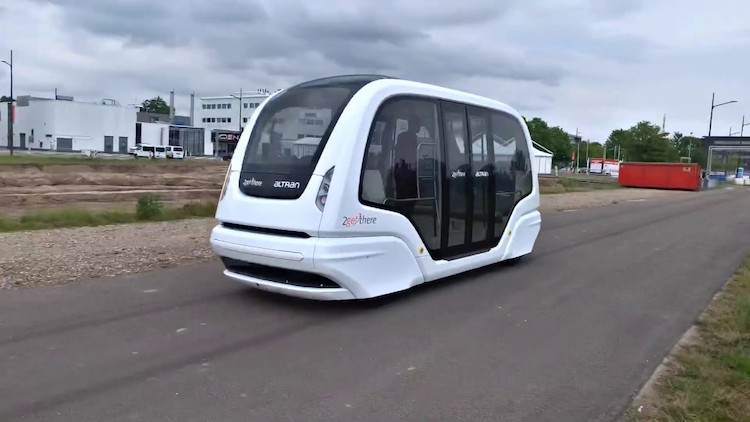

2getthere is a spin-off company of Frog Navigation Systems, which was founded in 1984 to deliver automated guided vehicles to factories.
The company became an independent company focused on autonomous vehicles for passenger transport in 2007, with a HQ in the Netherlands and was acquired by ZF Group, a German auto parts maker, in March 2019, which is one of the largest automotive suppliers.
Its business model is to sell the complete transportation system: vehicles and operation systems including a supervision system for fleet management, passenger interface, charging infrastructure and communication infrastructure.
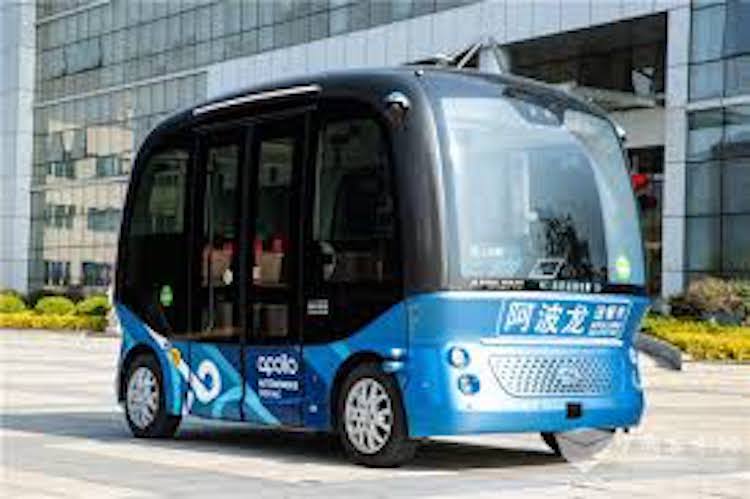

The Chinese tech giant Baidu was founded in 2000 and specializes in internet-related services and products, and AI. The company started the development of autonomous vehicles in 2013.
The company has negotiated 50 partners to sign up for the development and purchase of the new autonomous buses Apolong.
The volume production of the autonomous minibus Apolong is in partnership with Chinese vehicle manufacturer King Long who designs and manufactures the vehicle. In July 2018, Baidu announced its 100th Apolong, marking its ability to commercialize its autonomous shuttle buses.
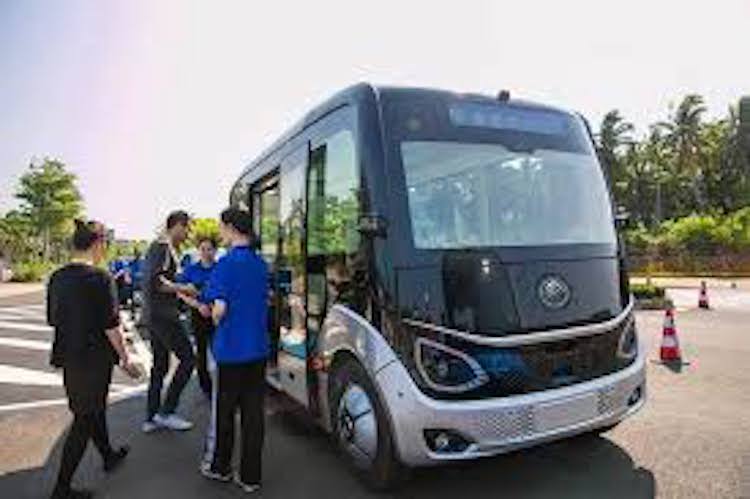

Yutong is a Chinese manufacturer of commercial vehicles, especially electric buses, headquartered in Zhengzhou, Henan. As of 2016, it was the largest bus manufacturer in the world by sales volume.
Yutong showcased their pure electric shuttle in March 2019 during a forum in Hainan, China, transporting attendees at the conference venue.
The autonomous shuttle integrates the U-Drive AI platform developed by UISEE, which uses sensor fusion and deep learning algorithms as well as a cloud-based vehicle management system.
The 5m-long shuttle has eight seats and can go up to 40km/h in a closed environment. The shuttle is equipped with a set of sensors including three lidars, radars, cameras and ultrasonics.
In May 2019, Yutong started a pilot project on 5G intelligent transportation, running five shuttles on an island district in Zhengzhou in collaboration with China Unicom and China Mobile. The tested district is covered with 5G and has a dedicated lane for autonomous shuttles.

