BMW shows off its smart factory technologies at its plants worldwide
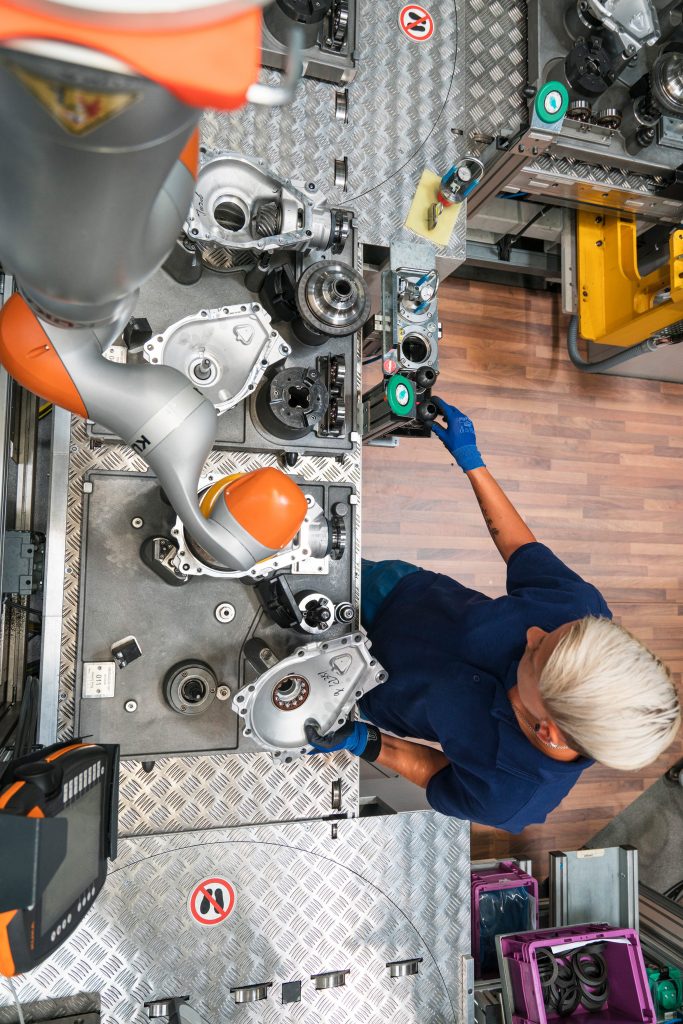

Collaborative robots, smart glasses, exoskeletons and innovative work gloves are among the tech being integrated at plants across the group’s worldwide operations
German automaker BMW has been providing a glimpse into the advanced manufacturing technologies at several of its factories – in Germany and the US.
The company says it has been harnessing the potential of innovative automation and flexible assistance systems in production.
In doing so, BMW says it has modernized the work environment and increased the efficiency of its workforce.
However, despite the high levels of automation, the company says people to remain “irreplaceable” due to cognitive abilities.

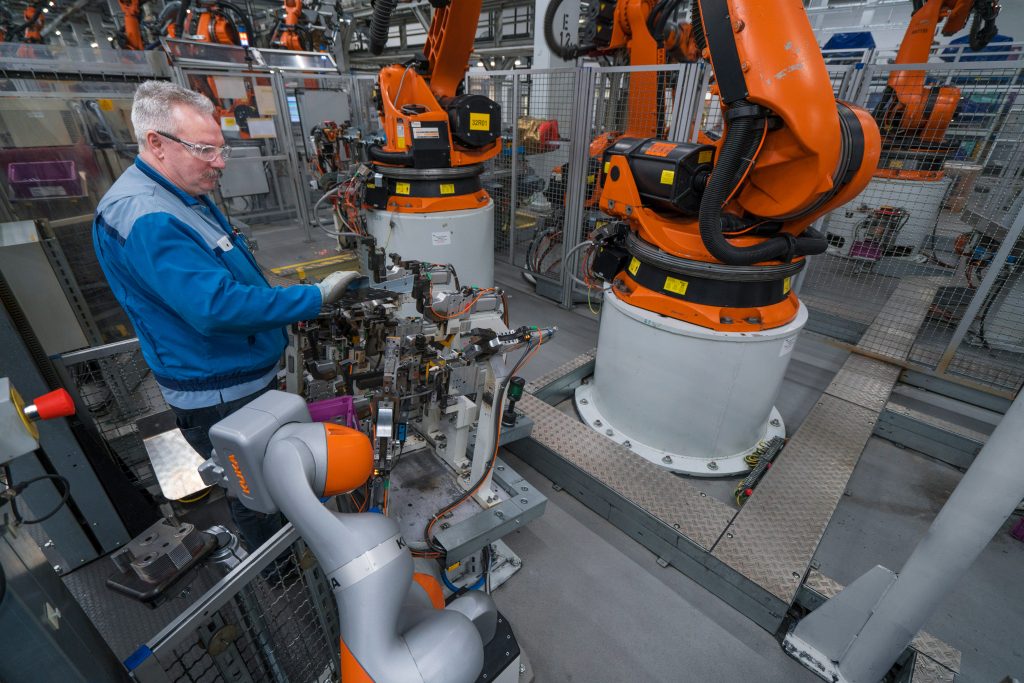
Nonetheless, BMW says it will have 60 “lightweight robots” in series operations by mid-year. By lightweight robots, it also means collaborative robots, some of which are manufactured, and other by Universal Robots.
BMW says the modernization of the work environment in the company’s production areas is a continuation of an ongoing policy of advancement.
Innovative automation and state-of-the-art assistance systems offer great potential for workstations, says BMW.
As a result, the company says it will be possible to further reduce ergonomically unfavourable and strenuous tasks, giving workers an opportunity to apply their unique cognitive skills to the best effect.
While in the past, man and machine worked in separated areas cordoned off by protective fences, the last few years have changed this setup: modern lightweight robots, smart devices and exoskeletons support workers as a direct part of people’s work environment in production, making the production system leaner and more adaptable.
Christian Dunckern, head of BMW production system, planning, toolmaking and plant engineering: “The digitalization allows the BMW Group to tap a growing range of options on how to advance the production system in many respects.
“People are more than ever becoming the designers of their own workplaces and can provide answers to the questions of an increasingly complex automotive production.”
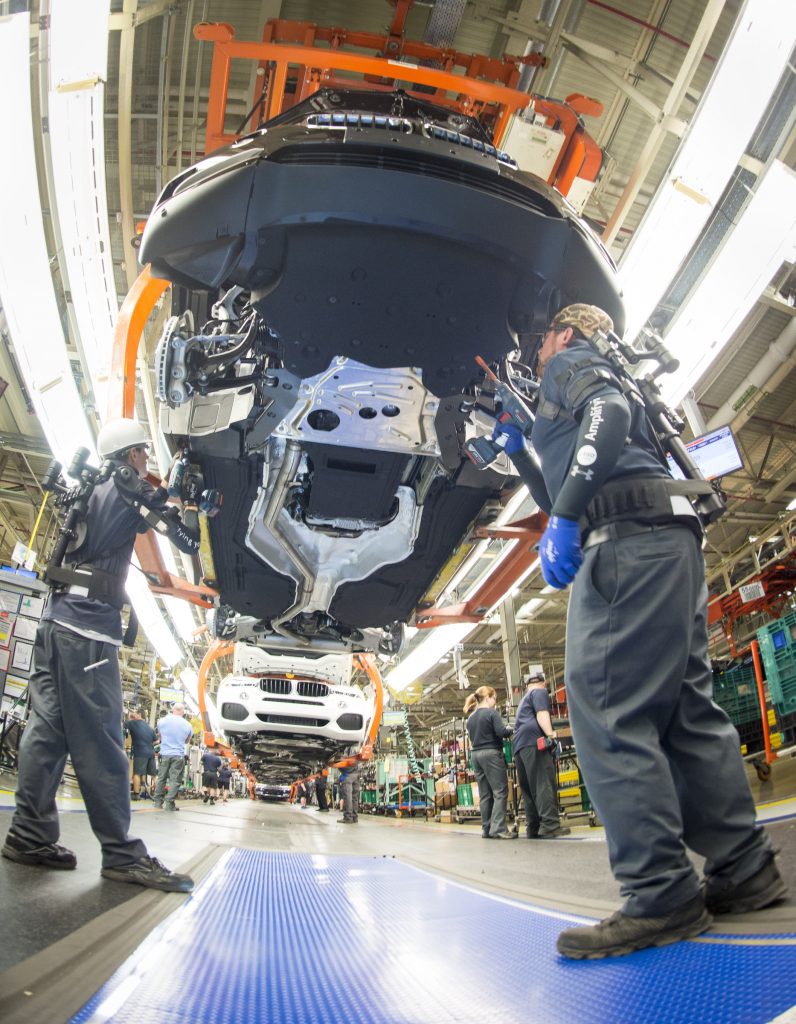

Purposeful application of assistance systems and lightweight robots
The allocation of roles between workers and available tools is clear: their high level of expertise, creative and cognitive skills make humans ideally suited for tasks that focus on actual value creation, specific precision work and quality management.
Assistance systems, on the other hand, support people in carrying out strenuous and repetitive tasks that constitute a stereotypical strain. In production, lightweight robots do not require any additional fixed points and are relatively mobile in where they can be applied.
Moreover, they can work directly with people. As a rule, the application of assistance systems is about finding reasonable solutions for the respective purpose, always with the focus on the specific benefit to be achieved.
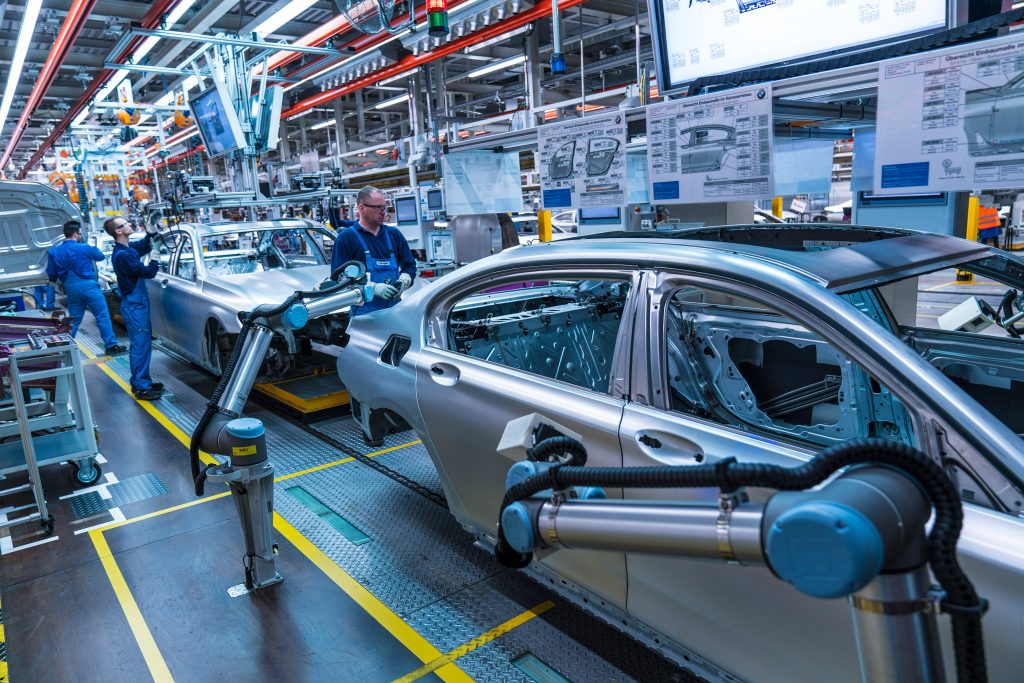

Man and machine bringing together their respective strengths
As early as 2013, the BMW Group commissioned a first lightweight robot that took its place among the workers at the assembly line of BMW plant, in Spartanburg, in South Carolina, USA.
Miss Charlotte, as the line crew calls its robot, is still in use mounting sound insulation to doors, but many things have changed since.
Today, over 40 lightweight robots are in use at the BMW Group plants; a total of 60 will be in operation by mid-year.
They assume tasks that would be physically strenuous for workers and often pose particular challenges due to the high level of precision required and the repetitiveness involved.
For instance, at BMW’s Dingolfing factory, in southern Germany, a ceiling-mounted lightweight robot in the axle transmission assembly lifts the bevel gears, which may weigh up to 5.5 kilos, and fits them accurately without any risk of damage to the gear wheels.
In this production area, workers and robots work together “hand in hand” in a confined space without any safety fences.
This collaboration gives people extra time to carry out tasks better suited to their capabilities while the lightweight robot applies exactly the force needed over a long period of time.
Safety sensors monitor the functions at all times and stop the process immediately if an obstacle is detected.
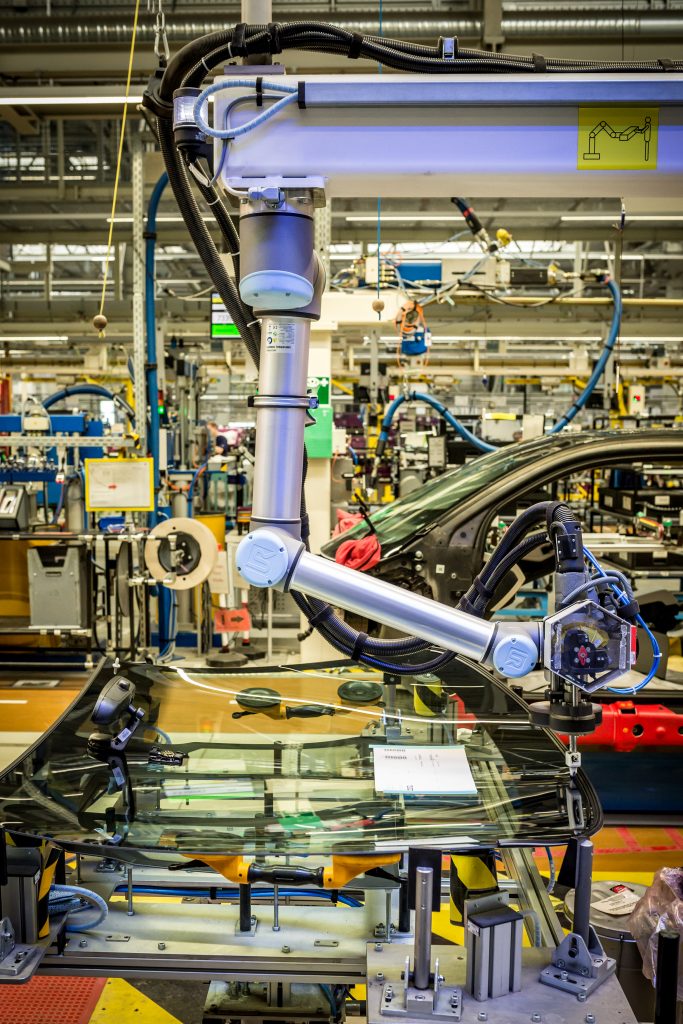
Equally demanding is the application of the adhesive to the front windows. What makes this task particularly challenging is that the viscous adhesive must be spread over the large glass surface in one go and without any fluctuation in film thickness.
At BMW’s factory in Leipzig, Germany, this task is carried out by a lightweight robot that works directly at the line with the human workforce.
But lightweight robots are also becoming more common in areas in which large robot facilities work behind safety fences.
Their flexibility, modest space requirements and high level of safety grant people access to areas that used to be off-limits.
Thanks to the broad range of possible applications, lightweight robots open up new potential in the field of traditional automation and give workers more leeway to implement improvements.
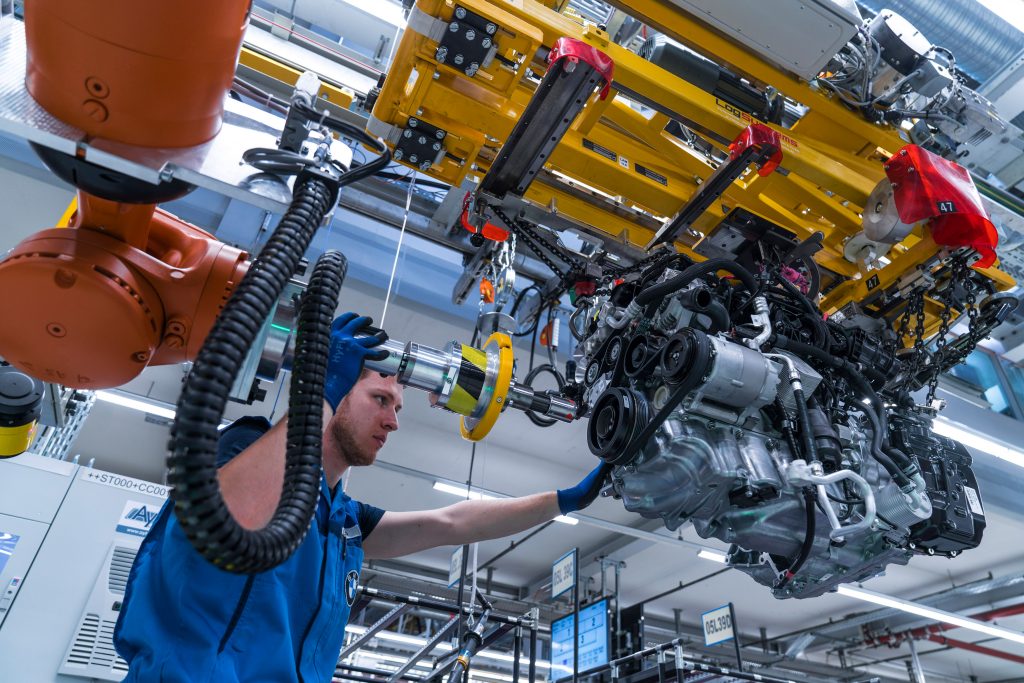
Today, direct man-machine cooperation is also possible with the traditional, large-scale industrial robots.
In the transmission installation unit at BMW’s Regensburg plant, in south-east Germany, a worker leads a large industrial robot to the screw bonding station.
While a laser-based system supports the process of placing the industrial robot, the exact position is determined by the trained worker. The idea for this application was developed by the on-site team itself.
Like in other use cases, safety is always the top priority: should a person get too close to the robot while the latter gets into position, state-of-the-art safety technology slows down the movement of the robot arm, if needed to a total standstill, before any danger can arise.
Due to the high forces required in the screw bonding process, this particular task cannot be assigned to a lightweight robot.

Digital production assistants to strengthen workers
Up until the beginning of the new millennium, phones were primarily used for making actual phone calls.
Today, they fulfil a great variety of functions. And just like our everyday living environment changes, so does the working environment in production.
Work gloves are fitted with barcode scanners on the back of the hand to omit the cumbersome steps of picking up the scanner, scanning an object and putting the device back.
The scan process is now triggered by the worker pushing a button on the index finger with the thumb.
This way, individual production processes can be improved and accelerated, leading to improvements in process quality and occupational ergonomics. About 230 of these innovative work gloves will be in use at the BMW Group before the end of the year.
Another example is the use of augmented reality applications on smart devices such as tablet computers, on which the image of a component can be overlaid with virtual specifications.
The tablet computer then compares and evaluates the actual and target states, allowing the worker to determine whether the part matches the target requirements and identify and resolve potential issues early on.
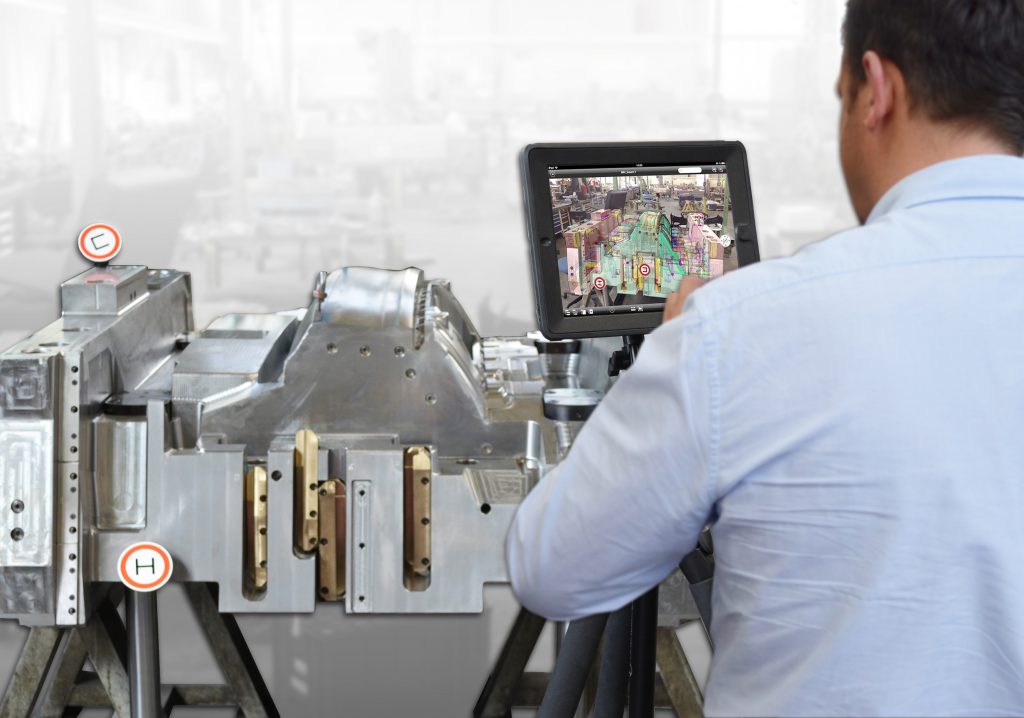

Augmented reality applications are applied at the BMW Group in early-phase concept validations, initial sampling inspections and tool acceptances at suppliers as well as in the maintenance of running systems.
Innovative exoskeletons worn directly on the body can act like a second skeleton, i.e. as an external support structure for the body.
The BMW Group uses both upper-body and lower-body exoskeletons.
The exoskeleton vest for the upper body strengthens the movement of the upper arms of people who have to carry out tedious tasks.
The vest’s joints have an integrated mechanical spring support that gives arms greater strength.
Twenty-four of these exoskeleton vests are currently in use in the series production of the BMW plant at Spartanburg; 44 more will be added over the course of the year.
Lower-body exoskeletons can be found in the production areas of several BMW Group plants in Germany.
Acting as a chair-type support, this kind of exoskeleton improves workers’ posture and offers relief in carrying out assembly tasks that require crouching or remaining in other positions that might affect people’s health.
On top of that, the leg support structure can transform prolonged standing into sitting and thus improve the comfort and flexibility of working conditions.
The exoskeleton consists of movable splints that can be affixed to the legs or torso and locked in different positions. At present, the BMW Group’s German plants use a total of 11 lower-body exoskeletons.

Efficiency and effectiveness at the workplace – more room for creativity
BMW says it aims to ensure an efficient, stable and flexible production through the use of all this advanced technology.
At the same time, the company pursues the goals of assigning staff according to people’s individual strengths and capabilities and of developing the work environment further.
Being spared particularly strenuous activities, workers have the time and energy to tackle more demanding and creative tasks.
Dunckern says: “In the time of smart devices and digitalization, we must still keep an eye on the added value the applied technology offers to the company.
“Nobody is better qualified to judge this than the people who actively shape our production system on a daily basis.
“This way, technology at the BMW Group actually serves the people and expands their creativity and efficiency.”

