The global humanoid robot market moved closer to large-scale commercialization in 2025, with installations reaching an estimated 16,000 units worldwide, according to new data from Counterpoint Research.
China accounted for more than 80 percent of all humanoid robot installations during the year, underlining the country’s dominant role in early deployments. Adoption was driven primarily by use cases in logistics, manufacturing, automotive, research, and data collection, the research firm said.
Chinese suppliers dominate early market
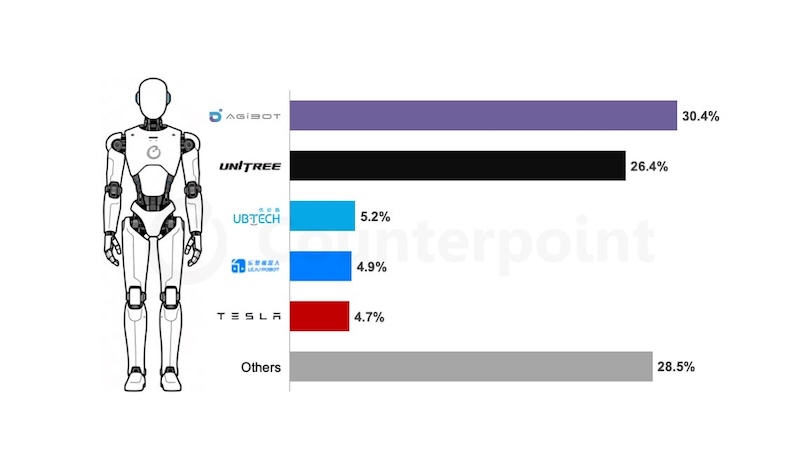
Shanghai-based startup AgiBot ranked first globally by annual installations in 2025, capturing around 31 percent of the market.
The company began mass production of its X2 and G2 humanoid robots last year and has deployed more than 5,000 units from its Shanghai factory across sectors including hospitality, entertainment, manufacturing, and logistics.
Unitree placed second with a 27 percent share, building on its background in quadruped robotics and motion control. The company has focused on developing lower-cost humanoid systems by producing key components such as motors, reducers, and sensors in-house.
UBTech ranked third with a share slightly above 5 percent. Its Walker-series humanoid robots are already being used on automotive factory floors, with a focus on collaborative industrial tasks.
Shenzhen-based Leju followed closely, also capturing around 5 percent of installations, supported by cloud-based training and software upgrades developed in partnership with Huawei Cloud.
Tesla entered the top five in 2025 with nearly 5 percent market share, driven by increased production of its Optimus Gen 2 and Gen 2.5 humanoid robots.
Counterpoint said Tesla’s involvement has had a broader impact on the humanoid robot supply chain, particularly in automotive manufacturing.
Together, the top five humanoid robot suppliers accounted for approximately 73 percent of global installations in 2025.
From prototypes to scaled production
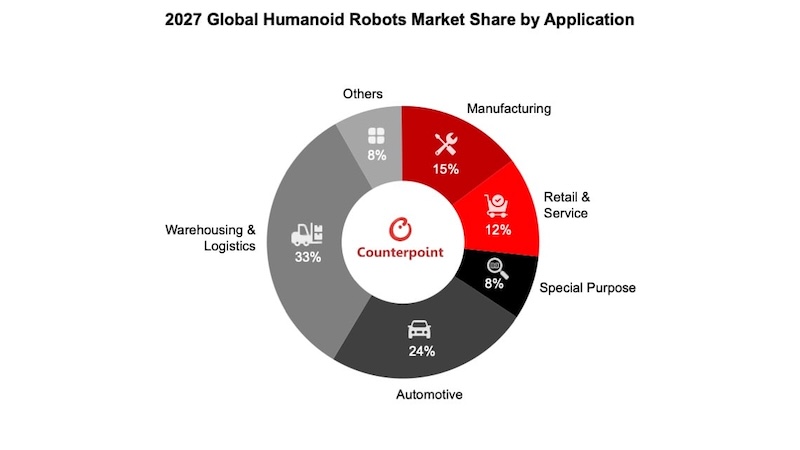
Counterpoint noted that 2025 marked a shift from experimental deployments toward early commercial rollouts, particularly in controlled industrial environments. The research firm expects cumulative humanoid robot installations to exceed 100,000 units by 2027.
By that point, logistics, manufacturing, and automotive applications are projected to represent about 72 percent of annual humanoid robot installations, reflecting the industry’s focus on structured, repeatable tasks rather than general-purpose consumer use.
Emerging business models and cost pressure
The report also highlighted several trends shaping the market’s next phase. Some Chinese companies are introducing lower-cost humanoid platforms aimed at interaction-focused use cases rather than industrial tasks, opening potential consumer and service-sector markets.
Robot-as-a-service (RaaS) models are also gaining traction, particularly in China, where companies are offering humanoid robots for rental in areas such as live performances, retail, and promotional events. Dedicated platforms to manage leased robots are expected to emerge as deployments scale.
At the same time, leading suppliers are expanding production capacity in an effort to reduce manufacturing costs.
Counterpoint pointed to aggressive automation plans by companies including Tesla and Figure AI, suggesting that humanoid robots may increasingly be used in the production of other robots and industrial systems.
While large-scale adoption remains several years away, the data suggests that humanoid robots are beginning to move beyond demonstrations and pilot projects, with industrial use cases likely to define the market’s near-term growth.