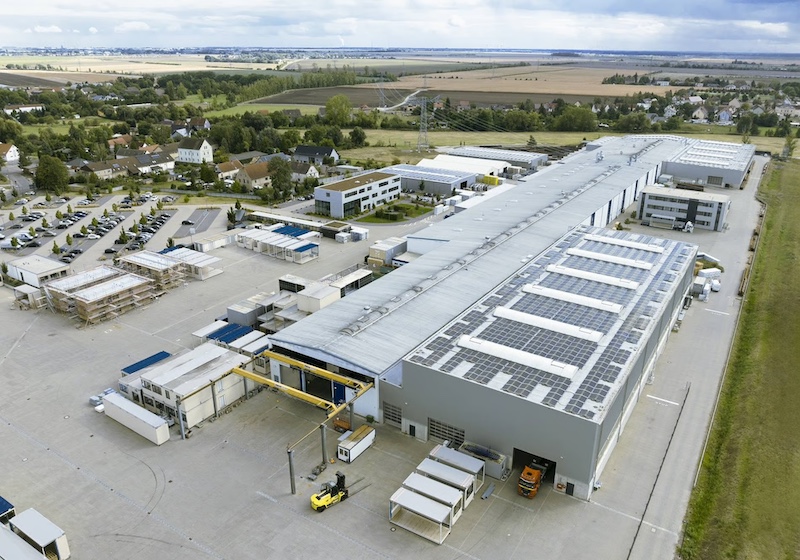
Industrial automation company Kuka and modular construction specialist Kleusberg have formed a partnership to bring advanced automation to modular construction, with the goal of modernising and streamlining manufacturing at Kleusberg’s plant near Halle (Saale).
The cooperation aims to install full robotic welding systems for floor and ceiling modules, forming part of a long-term plan to expand the use of automation in building production.
Beginning in 2027, Kleusberg will deploy a flexible, robot-based welding system supplied by Kuka. The turnkey line will use five industrial robots to weld more than 2,000 metres of 2D floor and ceiling frames every week across a production area of over 1,000 square metres.
The companies say the system has been designed to support highly customised manufacturing rather than mass-production of standardised units, with each robot programmed independently of the product type.
The approach aligns with the growing role of industrialised construction methods in the housing and public infrastructure sectors.
Oliver Hartmann, managing director of modular construction at Kleusberg, says: “In addition to increasing efficiency, improving working conditions played a significant role in the decision to automate, aiming to reduce health risks for employees caused by physically demanding postures. Furthermore, new technically oriented job roles are being created.”
Automation is expected to enhance both quality and safety. The system will conduct automatic collision checks before production starts and integrate seamlessly with other factory systems to maintain reliable operation.
Kuka says the robots will position components with high precision and verify welding quality with visual inspection tools.
Andre Zander, key account manager at Kuka Systems Assembly & Test, says: “Maximum precision is always the focus in robot-based automation. The system can position components exactly and visually inspect the weld seams for quality.”
Modular construction – also referred to as serial or system construction – uses prefabricated steel or wooden room modules produced in factory environments.
Proponents say the method offers improved cost certainty, predictable schedules, and faster project delivery compared to traditional on-site building, driven by industrial processes and increasing use of digital automation.