The researchers say the new system enables ‘smoother, more complex movements for next-generation robots’
Scientists in Japan, working in partnership with Fujitsu, say they have developed “an innovative method for efficiently controlling robot posture using quantum computing technology”.
The scientists involved are from the Shibaura Institute of Technology (Associate Professor Takuya Otani, Faculty of System Science and Engineering – Human Robot System Laboratory), and Waseda University (Professor Atsuo Takanishi, Faculty of Science and Engineering).
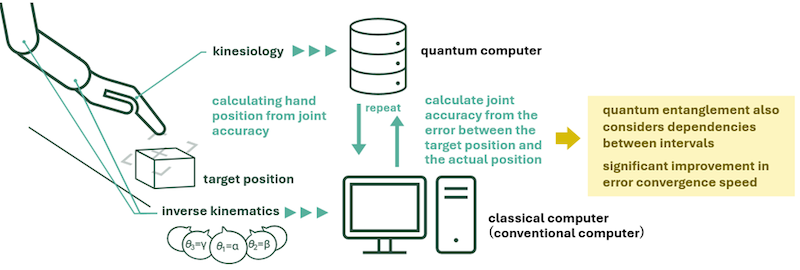
This new approach facilitates the efficient and accurate calculation of inverse kinematics; that is, determining joint angles from a target end-effector position, for multi-joint robots by leveraging qubit-based position representation and quantum entanglement.
Verification using Fujitsu’s quantum simulator achieved up to a 43 percent error reduction with fewer calculations compared to conventional methods. The effectiveness of quantum entanglement was also confirmed through an experiment carried out on the 64-qubit quantum computer jointly developed by Riken – a national scientific research institute in Japan – and Fujitsu.
By expressing the orientation and position of each robot link as a qubit, and by replicating the structural influence of parent joint movements on child joints through quantum entanglement, the number of necessary calculations was significantly reduced compared to conventional classical methods.
As quantum computing advances towards practical application, this development is expected to contribute substantially to the creation of next-generation robots that demand real-time control and complex operational capabilities.
Quantum technology breakthrough for complex robot posture calculation
In robot posture control, calculating inverse kinematics is crucial. For robots with multiple joints, the possible angle combinations are numerous, requiring iterative calculations to minimize the discrepancy from the target position and resulting in a high computational load.
For a full-body multi-joint model with 17 joints, equivalent to the number of joints in the human body, the number of possible calculations required are too vast to be solved directly. A common approach has been to perform motion calculations with an approximated 7 joints, but this limits the smoothness of movement.
In this research, a new method leveraging the power of quantum computing has been proposed to address these challenges. The orientation and position of each robot part (link) are represented by qubits, and forward kinematics; that is, calculation of end-effector position from joint angles, is carried out using quantum circuits.
Inverse kinematics calculations are performed on classical computers, achieving efficient posture control through a hybrid quantum-classical approach.
Improved convergence speed and accuracy with quantum entanglement
Furthermore, by introducing quantum entanglement, the structure where the movement of parent joints naturally influences child joints is reproduced on the quantum circuit.
This significantly improved the convergence speed and accuracy of inverse kinematics calculations. In addition, a trial calculation showed that motion calculations for a full-body multi-joint model with 17 joints can be executed in approximately 30 minutes.
Expected applications in humanoid and multi-joint robots
This method can express the posture of multi-joint robots with a small number of qubits, making it implementable even in current noise intermediate-scale quantum (NISQ) computers.
In the future, this technology could be applied to real-time control of humanoid robots and multi-joint manipulators, obstacle avoidance, and energy optimization. Further performance improvements are also anticipated through combination with advanced quantum algorithms such as quantum Fourier transform.